
The new facility builds on a long-standing collaboration between BU and the commonwealth, that includes the construction in Holyoke, with several other partners, of the Massachusetts Green High Performance Computing Center.
Read this story at BU Today
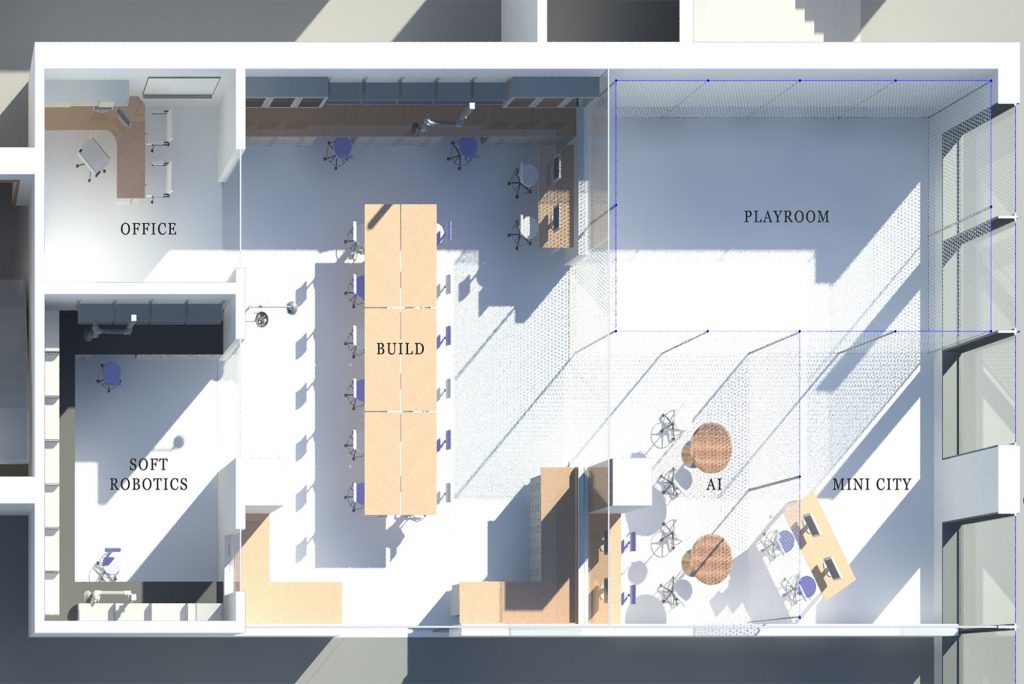
It’s a “playroom” for Boston University students to operate robots on the ground—and in the air. It’s a “brain” space to research robots that think. It’s a miniaturized city for road testing mini self-driving vehicles. It’s an area to work on lifesaving, flexible medical robots that don’t require motors or rigid parts.
BU undergraduates and master’s students, heretofore largely shut out of the University’s tight robotics laboratory space, will now be able to explore the robotics world at a new College of Engineering lab. The $8.8 million, 2,000-square-foot Robotics and Autonomous Systems Teaching and Innovation Center (RASTIC), to be sited in the former CVS building at 730 Commonwealth Ave., will open in summer 2023.
It will be funded 50-50 by the University and the Massachusetts Technology Collaborative (MassTech), a public agency supporting the state’s tech sector. Mike Kennealy, Massachusetts secretary of housing and economic development, announced the grant at a news conference May 4 at the BU Photonics Center, flanked by University and state leaders, including Robert A. Brown, president of BU, and Kenneth Lutchen, dean of ENG.
“The new tools we’re investing in today,” Kennealy said, “will allow students to design and launch their own R&D projects, and for companies in the region, it will create a neutral space for research that’s focused on robotics and autonomous solutions, and work with BU students and faculty to design, prototype, and test new devices.” He said the lab will also host kindergarten-through-12th grade students in a tech scholars program.
“This is really, really good work, and really important work,” he said. “This is a fabulous example of that work, and it really is critical to the future of our state in a lot of ways….We have to continue to be among the most innovative places in the world.”
Brown called the lab “a perfect illustration of what happens when this kind of force of imaginative leadership” in academia and industry “meet together with a state that has got the vision and foresight to support the kind of innovation that we’re doing.” He quipped that Kennealy, who once worked in private equity, “knows something about placing bets, which he’s now doing today.”
MassTech has awarded about 10 such grants among a field of 26 applicants, said Pat Larkin, director of MassTech’s grant-making Innovation Institute. RASTIC “clearly rose to the top,” he said, and “we felt, scored on many of the metrics that are important to us.”
With RASTIC, BU will more than quadruple its master’s degree students in robotics, Larkin said, boosting Massachusetts’ competitiveness with rivals from Silicon Valley to China: “We have a real appetite to address the talent challenges that exist in this state that are critical to the future of our tech and innovation economy….The number-one constraint in every emerging sector that we work with in Massachusetts is the human capital to build on the asset that exists.
“The students that come out of BU RASTIC we anticipate being the actual innovators of the future,” he said. “They are going to gain an experience there that’s going to inspire new ideas, new innovations, new opportunities for start-ups and new business formation in the state.
“The commonwealth has a robust, globally significant robotics sector,” Larkin added. “And to build capabilities both on the technology side and on the talent side really feeds the flywheel in Massachusetts for robotics.”
He said the expectation is that the team at BU will help take the robotics cluster in Massachusetts “to the very next level.”
Ioannis Paschalidis, an ENG Distinguished Professor of Engineering and of computing and data sciences, drafted the RASTIC proposal that won the grant with Sean Andersson, an ENG professor of mechanical and systems engineering. (Paschalidis directs BU’s Center for Information and Systems Engineering, the organizational home of RASTIC.) “A lot of robotics research takes place in EPIC,” BU’s Engineering Product Innovation Center, he says. But “we have undergraduate students in electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, [and] there is no capacity there” for them or for master’s students.
In particular, Paschalidis says, ENG’s master’s program in robotics and autonomous systems, which has an experiential component, gets roughly 300 applications a year, but can select only about 20. “We don’t have the capacity to support many of these projects,” he says. “We need a place where the students can go in, can engage, industry can come in and be affiliated sponsors of specific projects that students at the master’s and at the undergraduate level can do.”
A student in that program, Nash Elder (ENG’23), agrees. He works with folding robots inspired by origami, and “having the means to fabricate hardware, access software backed by computing power, and collaborate with other students is an empowering resource,” he said. “I could see the space really as a central hub for the roboticists of BU.”
BU will hire a professor to direct RASTIC, which will also have space for BU researchers with robotics grants to translate their ideas into practical applications. Among the areas researchers and students will test at the new lab, Paschalidis says, are these:
RASTIC builds on a long-standing collaboration between BU and the commonwealth, Larkin said, including the construction in Holyoke, with several other partners, of the Massachusetts Green High Performance Computing Center.
“Boston University has been a good partner to the state over many years,” he said. “The key personnel at BU—they understand the mission of the state. These investments are about growing the economy….Our university infrastructure really represents our comparative advantage as an economy globally.
“We don’t grow corn. We don’t have oil. We have people.”
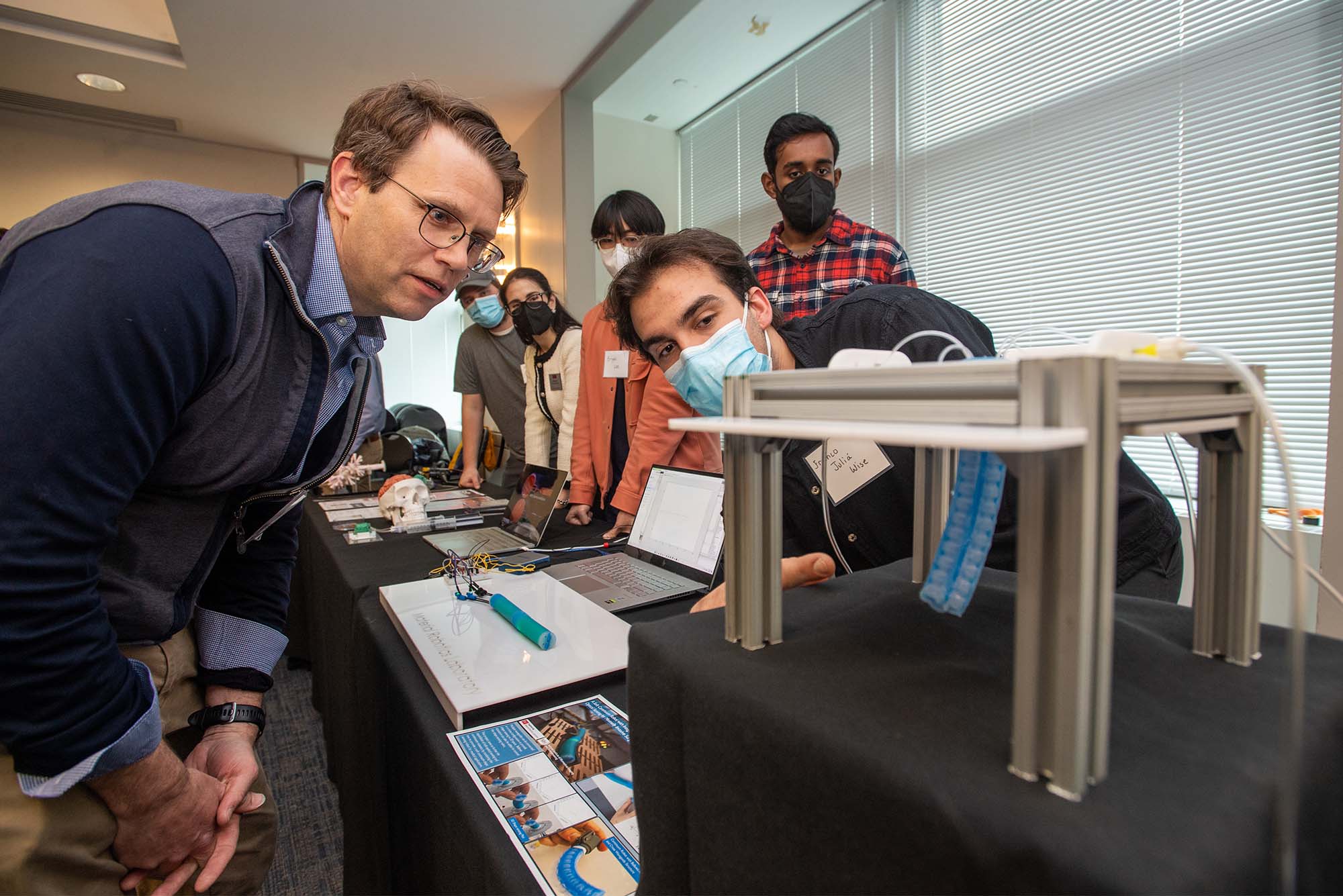
Story image: After the press conference announcing BU RASTIC, students demonstrated the types of robotics work that will be done in the new lab. Franco Julia Wise (ENG’22) (right) explains the workings of his team’s Soft Robot with Integrated Soft Optical Sensing for Minimally Invasive Surgery to ENG’s Sean Andersson (left) - Image courtesy BU News