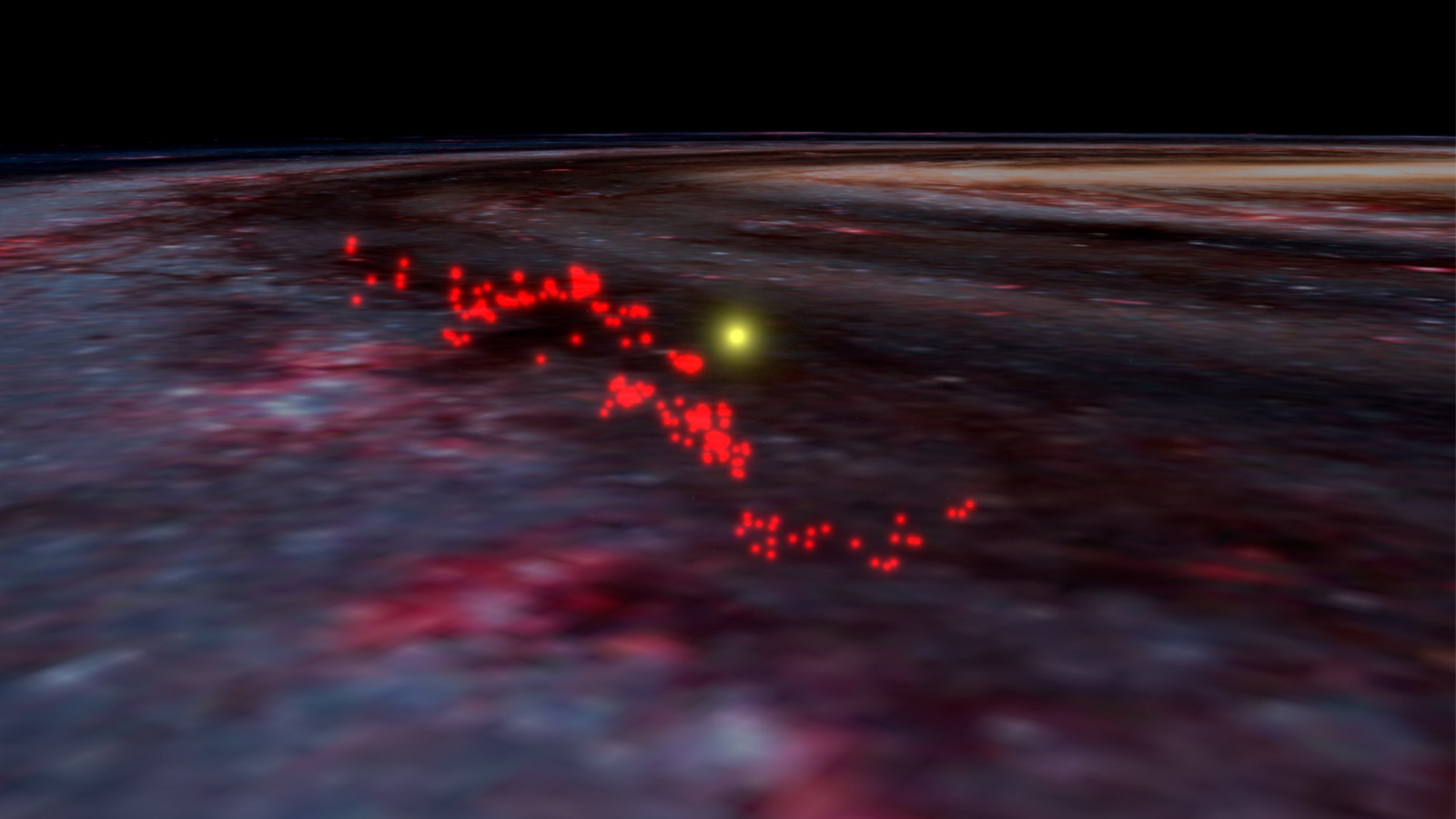
Harvard astronomers using computers housed at the MGHPCC discover largest known coherent gaseous structure in our galaxy.
Astronomers at Harvard University have discovered a monolithic, wave-shaped gaseous structure - the largest ever seen in our galaxy - made up of interconnected stellar nurseries. Dubbed the “Radcliffe Wave” in honor of the collaboration’s home base, the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study, the discovery transforms a 150-year-old vision of nearby stellar nurseries as an expanding ring into one featuring an undulating, star-forming filament that reaches trillions of miles above and below the galactic disk.
The work, published in Nature, was enabled by a new analysis of data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia spacecraft, launched in 2013 with the mission of precisely measuring the position, distance, and motion of the stars. The research team’s innovative approach combined the super-accurate data from Gaia with other measurements to construct a detailed, 3D map of interstellar matter in the Milky Way, and noticed an unexpected pattern in the spiral arm closest to Earth.
Computations were enabled using Harvard University's Odyssey computing cluster housed at the MGHPCC.
Read more at the Harvard Gazette
Story image: In this illustration, the "Radcliffe Wave" data is overlaid on an image of the Milky Way galaxy. Image from the WorldWide Telescope, courtesy of Alyssa Goodman via The Harvard Gazette.
João Alves, Catherine Zucker, Alyssa A. Goodman, Joshua S. Speagle, Stefan Meingast, Thomas Robitaille, Douglas P. Finkbeiner, Edward F. Schlafly and Gregory M. Green (2020), A Galactic-scale gas wave in the solar neighborhood, Nature, doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1874-z
Catherine Zucker, Joshua S. Speagle, Edward F. Schlafly, Gregory M. Green, Douglas P. Finkbeiner, Alyssa Goodman, João Alves (2020), A compendium of distances to molecular clouds in the Star Formation Handbook, arXiv: 2001.00591 [astro-ph.GA]